When managing business travel, financial clarity is essential to streamline operations and optimize budgets, two terms that often confuse this context are expense and expenditure. While they might appear similar, they serve distinct accounting and financial reporting purposes. Understanding the difference between expense and expenditure can help businesses. You accurately categorize costs, improve decision-making, and maintain compliance.
Expenses often involve recurring costs like meals, accommodations, or transportation. These are short-term costs reflected in a company’s income statement. Expenditures are broader. They encompass long-term investments such as purchasing travel management software or fleet vehicles. This distinction helps companies improve financial planning and decision-making.
Misunderstanding the terms expense and expenditure can lead to issues that can impact the company’s bottom line. In this guide, we’ll help you understand what is expense, expenditure, and the differences between them. We will also emphasize how these concepts play a critical role in managing corporate travel budgets effectively.
What is Expense?
An expense refers to any money spent or cost incurred by a business daily for earning revenue. Expenses are recurring and short-term arrangements which directly affect the business’s primary activities. They are recorded in a company’s profit and loss statement, thus reducing its net income for the period.
In business travel, expenses include costs such as airfares, hotel stays, meals, and transportation. This is usually done by an employee who incurs costs for carrying out business-related activities. Each expense will be classified according to the operational necessity and is vital for understanding a company’s operational performance and profitability.
Characteristics of Expenses
- Short-term impact: Expenses provide instant or short-lived benefits, such as a single business trip, or monthly payments toward a travel management solution.
- Recurring nature: They are often and regularly incurred. These expenses remain cash ongoings for operational necessity.
- Direct revenue association: The expenses relate to the generation of revenue: travel for meeting new clients or travel to attend a conference.
- Tax implications: Most expenses are deductible from taxable income, reducing the company’s overall tax liability.
What is an Expenditure?
An expenditure consists of a sizeable distribution of cash by a company, usually to create, maintain, or satisfy long-term needs to acquire. Other names for these outlays are nonrecurring. This allows for benefits beyond the accounting period used in generating income statements. In contrast to expenses, expenditures do not directly impact the financial statements. They rather are placed on the balance sheet and expensed over time as depreciation or amortization.
Investments in travel management software, company vehicles, or accommodation facilities are some examples of expenditures in business travel. The purpose of these investments is to support enabling operations and long-term business objectives.
Characteristics of Expenditures
- Long-term impact: These expenditures lead to a long-term improvement in company growth and productivity.
- Non-recurring nature: They usually denote single or infrequent financing commitments.
- Asset creation or enhancement: Expenditure mostly leads to the purchase of assets or the enhancement of existing assets.
- Capitalization: They are recorded as assets on the balance sheet and depreciated or amortized over their useful life.
You may also like: 9 Tips for Efficient Expenditure Management
Calculate your savings now!
The Key Difference Between Expense and Expenditure
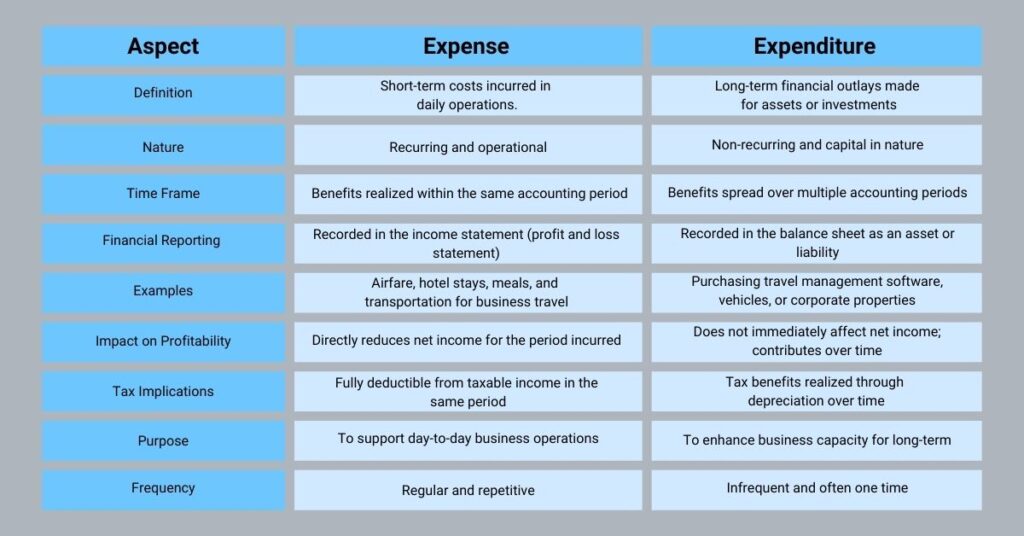
After understanding what is expense and expenditure, let us look at the difference between expense and expenditure.
1. Definition and Nature
Expense
An expense is a cost incurred in the daily operations of a business. It is the short-term outflows from money directly related to revenue generation and day-to-day functioning. These include expenses such as travel reimbursement, meals, or hotel accommodations during business trips.
A classic example of expense is when a manager pays for a taxi ride to attend a client meeting.
Expenditure
Expenditures are cash outlays made by a business for acquiring or improving an asset, service, or final product. Unlike expenses, expenditures are generally non-repetitive, as they lead to the acquisition or improvement of existing assets. These benefits are enjoyed by the business for a longer period.
2. Time Frame
Expense:
- Short-term in nature, with benefits realized within the same accounting period (e.g., monthly or quarterly).
- Regular and recurring, such as employee travel expenses during ongoing projects.
Expenditure:
- Long-term, with benefits extending over multiple accounting periods.
- Examples include significant investments, such as building an in-house accommodation facility for traveling employees.
3. Financial Reporting
Expense:
- Recorded in the income statement (also known as the profit and loss statement).
- Reduces the company’s net income and reflects the cost of running operations within a specific period.
Expenditure:
- Recorded in the balance sheet as an asset or liability.
- Expenditures for assets are either capitalized and gradually depreciated or amortized over their useful life (e.g., the cost of a vehicle purchased for business travel).
4. Types of Costs Involved
Expense:
- Includes operational and administrative costs, such as:
- Airfare for employees.
- Lodging expenses during business trips.
- Per diem allowances for meals.
Expenditure:
- Includes capital and non-operational costs, such as:
- Purchasing new software or tools to manage travel processes.
- Upgrading infrastructure to accommodate frequent travel needs.
5. Impact on Financial Health
Expense:
- Directly impacts a company’s profitability during the period it is incurred.
- Overspending on expenses can reduce net income and indicate inefficiencies in operations.
Expenditure:
- Impacts the company’s cash flow initially, but its benefits are spread out over time.
- Strategic expenditures, such as investing in travel management platforms, can improve long-term operational efficiency.
6. Tax Implications
Expense:
- Fully deductible from taxable income in the accounting period in which they are incurred.
- For example, travel expenses such as air tickets and hotel stays are often categorized as operational costs and deducted from taxable profits.
Expenditure:
- May offer tax benefits through depreciation or amortization over time.
- For example, a company-owned vehicle purchased for business travel might be depreciated over its expected useful life, providing incremental tax benefits.
7. Examples in Action
Scenario 1: Business Travel for a Conference
Expense:
- Airfare for employees traveling to attend the conference.
- Meals and lodging during the trip.
Expenditure:
- Investing in travel insurance for all employees attending business trips annually.
Scenario 2: Implementing Travel Management Technology
Expense:
- Paying a monthly fee for using a cloud-based travel booking tool.
Expenditure:
- Purchasing proprietary software that automates travel booking and expense tracking.
Know the Difference between Expense and Expenditure
Primarily, expense and expenditure differ in scope, purpose, and effect it has on the business financial statements. While expenses concern daily operations and cover the short-term usage cost, expenditures deal with long-term investments aimed at enhancing the company’s capacity or infrastructure. Acknowledging this distinction is key to successful financial accounting, budgeting, and planning when it comes to business travel.
To manage your expenses efficiently, you must invest in a TMC such as itilite. It is a new-age TMC that helps businesses in:
- Track spending patterns
- Set and monitor budget goals
- Identify cost savings
- Expense reporting and reimbursement
- Seamless integrations
Book a free demo with us to streamline your finances.








