Running a business involves several financial activities, and managing your business expenses is one of the most important aspects. For any company, whether it’s small or large, understanding and controlling these expenses is essential not just for sustaining profitability but also for optimizing operations, forecasting future growth, and staying compliant with tax regulations.
Effective expense management plays a critical role in maintaining healthy cash flow, identifying areas for cost-cutting, and enabling you to make strategic financial decisions that benefit the overall business. Without proper management of expenses, even the most profitable businesses can struggle to keep up with operational costs and unforeseen financial challenges.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about business expenses, from understanding the various types to creating a detailed list of common expenses. We’ll also cover how to track these costs efficiently and share best practices to help you manage your business expenses effectively, ensuring financial stability and long-term success.
What Are Business Expenses?
Business expenses are the costs a company incurs in its day-to-day operations. These expenses include everything from employee salaries, rent, and office supplies to more complex costs like marketing, legal fees, and travel. Business expenses are typically tax-deductible, reducing a business’s overall taxable income, provided they are deemed ordinary and necessary.
Tracking and managing business expenses is a key component of financial planning and budgeting. It helps companies keep their finances in order, forecast future costs, and ensure they are operating within budget.
Types of Business Expenses
Business expenses can be categorised in several ways, one of the most common being based on frequency and function. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses organise their financial tracking and ensure that each type of expense is managed appropriately.Hence it is important for companies to make a list of expenses.
1. Types of Business Expenses Based on Frequency
a) Fixed Expenses
Fixed expenses are the costs that remain constant and occur regularly, regardless of the business’s level of production or sales activity. These expenses are predictable and usually recur monthly, quarterly, or annually. Because of their consistent nature, businesses can budget for them easily.
Fixed expenses provide stability in budgeting but must be managed carefully, as they represent ongoing financial obligations.
Examples of fixed expenses include:
- Rent or lease payments: These are made for office space, warehouses, or other business premises.
- Salaries: Payment to full-time employees remains the same each pay period, regardless of how much revenue the company generates.
- Insurance premiums: Monthly or yearly payments for business insurance, health insurance, or liability insurance.
- Loan repayments: Fixed installments paid toward business loans or mortgages.
b) Variable Expenses
Variable expenses are business expenses that change depending on the level of business activity. They fluctuate with the production or sales volume and are harder to predict. This is because they depend on customer demand or operational levels.
Variable expenses are typically more flexible and can be controlled more easily during periods of low revenue.
Examples of variable expenses include:
- Raw materials or inventory costs: The cost of purchasing supplies or materials increases when production ramps up and decreases when sales slow down.
- Shipping and delivery costs: Expenses related to shipping products can fluctuate based on the volume of orders processed.
- Commissions and bonuses: Employee compensation tied to sales performance will rise and fall with the company’s success.
- Utilities: Bills for electricity, water, and other utilities may vary depending on seasonal use or business hours.
c) Periodic Expenses
Periodic expenses occur irregularly, such as once a year or at different times throughout the year. These business expenses may be planned, like an annual renewal, or unplanned, such as emergency repairs. Periodic expenses are less predictable and can create cash flow challenges if not planned for adequately.
Examples of periodic expenses include:
- Annual software license fees or subscriptions: Many businesses use software or platforms that charge yearly instead of monthly.
- Repairs and maintenance: Unexpected repairs to equipment or facilities.
- Taxes: Some business taxes, such as property tax or corporate income tax, are due at specific times of the year.
d) One-Time Expenses
One-time expenses are non-recurring costs that occur only once or infrequently. These are often unexpected or related to specific projects, investments, or unique business situations. Proper planning for one-time expenses can prevent them from disrupting the company’s cash flow.
Examples of One-Time Expenses:
- Purchasing new equipment: A one-time investment in new machinery, computers, or office furniture.
- Legal fees: Costs related to a lawsuit, a merger, or the drafting of new contracts.
- Research and development (R&D): One-off investments in developing new products or services.
Relocation costs: Expenses incurred when moving to a new office or expanding to a new location.
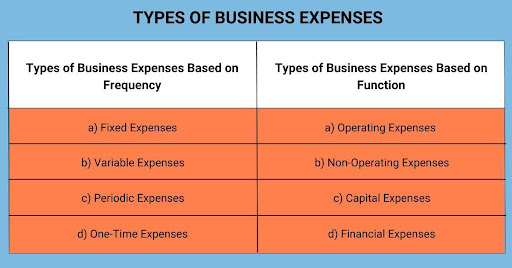
2. Types of Business Expenses Based on Function
a) Operating Expenses
Operating expenses (also known as OPEX) are the costs required for the day-to-day running of the business. These expenses are necessary for generating revenue and are often either fixed or variable. Operating expenses are essential for keeping the business functional, productive, and competitive. Operating expenses are ongoing, and managing them effectively is crucial for maintaining profitability.
Examples of operating expenses include:
- Office supplies: Basic materials like paper, pens, computers, and office furniture.
- Utilities: Electricity, water, heating, and internet services required to run the business.
- Marketing and advertising: Costs associated with promoting products or services through various channels, such as digital ads, print media, or social media campaigns.
- Payroll: Salaries and wages paid to employees, along with associated benefits like healthcare and retirement plans.
b) Non-Operating Expenses
Non-operating expenses are costs that are not directly related to the business’s primary operations. These business expenses are often unusual or unrelated to the production or sales of goods and services but still must be accounted for in the company’s financial statements.
Examples of non-operating expenses include:
- Interest expenses: Payments made on loans or lines of credit taken out by the business.
- Currency exchange losses: Losses incurred due to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates, often experienced by businesses with international dealings.
- Legal expenses: Costs associated with lawsuits, settlements, or fines.
c) Capital Expenses
Capital expenses (also known as CAPEX) involve the acquisition or improvement of long-term assets, such as buildings, equipment, or technology. These assets are expected to provide value over an extended period, and their cost is depreciated over time.
Capital expenses are typically large and planned out in advance. Since they represent long-term investments, they must be strategically managed to ensure the business gains maximum value from them.
Some of the capital expenses include:
- Purchase of equipment: The office expenses list is about buying machinery, computers, or vehicles that the business will use for multiple years.
- Building renovations or construction: Improving or expanding facilities to accommodate growth.
- Technology investments: Buying new software or upgrading hardware that enhances business operations.
d) Financial Expenses
Financial expenses are costs related to borrowing funds or other financial activities. Such business expenses occur when a business raises capital or incurs debt and must pay interest or fees as a result. While financial expenses are necessary for raising capital, businesses aim to minimise these costs to maintain healthy financial performance.
Examples of financial expenses include:
- Interest on loans: Any payments made toward interest on business loans or lines of credit.
- Bank fees: Charges for business banking services, such as wire transfers, overdrafts, or account maintenance.
- Credit card fees: Interest or fees incurred on business credit card transactions.
How to Track Business Expenses?
Tracking business expenses is essential for financial management. It ensures that companies stay organised, make informed decisions, and remain compliant with tax laws. Here’s how you can track your company expenses effectively:
1. Use an Accounting System
Accounting software like QuickBooks, FreshBooks, or Xero can automate much of the expense tracking process. These tools categorise expenses, link them to bank accounts, and generate reports that make it easy to review your financials. You can also track income, generate invoices, and reconcile bank statements.
2. Separate Business and Personal Finances
Always separate personal and business finances. Mixing the two can cause confusion and make it difficult to track expenses accurately. Use a dedicated company expense credit card and bank account to ensure clear and separate records. This also simplifies tax filings and helps avoid issues with the IRS.
3. Track Receipts and Documentation
Maintain a clear record of all receipts and documentation related to your business expenses. Whether using a digital filing system or a physical filing cabinet, keeping thorough records is essential for tax purposes and for verifying expenses in case of an audit.
4. Use Expense Management Tools
Consider using specialised expense management software to simplify the tracking process. Tools like itilite allow employees to submit expenses, track spending in real-time, and generate reports. These tools integrate with accounting software, further streamlining the process.
5. Create Expense Categories
Organising your expenses into categories (e.g., marketing, travel, office supplies etc) helps you track how much you’re spending in different business areas. This makes it easier to analyse trends, identify areas for cost-cutting, and plan budgets effectively.

Common Business Expenses List:
It’s crucial to have a clear understanding of the common expenses that most businesses face. Below is a list of expenses that can serve as a reference when managing your own company’s finances:
1. Employee Salaries and Benefits
Paying your employees is likely one of the largest expenses your business will incur. This includes base salaries, bonuses, health insurance, retirement contributions, and other benefits.
2. Office Rent or Mortgage Payments
For businesses that have a physical office space, rent or mortgage payments will typically be one of the largest fixed costs. These expenses are predictable and recurring.
3. Utility Bills
Utilities such as electricity, water, heating, and internet services are essential for day-to-day operations. These business expenses can vary depending on the season and usage.
4. Supplies and Equipment
This includes your office expenses list—everyday items like paper, pens, computers, printers, and other essential equipment. Depending on the industry, this could also include specialised machinery or tools.
5. Marketing and Advertising
Marketing and advertising expenses can vary greatly, but they are essential for promoting your products or services. This includes online advertising, social media marketing, public relations, and paid ads.
6. Insurance
Businesses need various types of insurance, such as general liability, property insurance, or health insurance for employees. These costs protect your company from unforeseen events.
7. Professional Fees
Professional services, such as legal advice, accounting services, and consulting, can be a significant part of your company office expenses list. These business expenses are essential for ensuring compliance with regulations and optimising business performance.
8. Travel and Entertainment
Travel expenses, especially for client meetings, conferences, and business trips, can add up quickly. This includes airfare, hotel accommodations, meals, and other travel-related costs.
Benefits of Business Expenses
Business expenses, while an inevitable part of running a company, offer several benefits that can enhance operational efficiency, productivity, and long-term profitability. Effectively managing and tracking business expenses can provide a competitive edge and support a company’s growth. Below are the key benefits associated with business expenses:
1. Tax Deductions
One of the most significant benefits of business expenses is that many of them are tax-deductible. This means businesses can reduce their taxable income by deducting necessary and ordinary expenses related to their operations.
By ensuring proper documentation and understanding which expenses are deductible, businesses can capitalise on tax benefits and reduce their financial burden. Deductible expenses may include office supplies, travel expenses, employee wages, utilities, and more. Some advantages include:
- Lower taxable income: Reducing taxable income helps businesses save money during tax season, which can be reinvested into the company.
- Maximising profits: Deductions minimise the amount of tax payable, leaving more funds available for operations or future growth.
2. Improved Financial Management
Tracking and managing business expenses fosters better financial control and planning. Better financial management ensures long-term sustainability and allows companies to make informed decisions that optimise their resources. When companies have a clear understanding of their expenditures, they can:
- Forecast future costs: By analysing previous spending, businesses can make accurate budget forecasts and plan for future expenses.
- Manage cash flow effectively: Knowing where money is being spent helps in maintaining a healthy cash flow, ensuring that there are enough funds to cover operational needs.
- Identify cost-saving opportunities: Tracking expenses can highlight inefficiencies or unnecessary expenditures, helping businesses cut costs.
3. Enhanced Budgeting and Planning
Business expenses provide crucial insights for accurate budgeting and financial planning. Having a well-defined budget ensures that companies can operate within their means while preparing for future opportunities and challenges.
By categorising and regularly tracking expenses, companies can:
- Set realistic budgets: Understanding both fixed and variable types of expenses enables businesses to set more accurate budgets.
- Plan for growth: With a clear view of expenditures, companies can allocate funds for investments, marketing, hiring, and expansion.
- Avoid overspending: Tracking expenses helps prevent unplanned or unnecessary expenditures, keeping the business financially stable.
4. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Certain types of expenses—such as investments in technology, employee training, or office equipment—can directly lead to improved efficiency and productivity. For instance:
- Technology investments: Tools like project management software, cloud services, or customer relationship management (CRM) systems can streamline processes and increase productivity.
- Employee training: Investing in employee development ensures that the team is equipped with the necessary skills to perform tasks more efficiently.
- Office upgrades: Comfortable and modern office equipment can enhance employee morale, leading to higher job satisfaction and output.
Allocating business expenses toward tools and resources that improve performance can result in greater productivity and better outcomes.
5. Better Business Decision-Making
A detailed understanding of business expenses enables better decision-making, as companies can assess the impact of various expenditures. With accurate expense tracking, businesses can make data-driven decisions that lead to greater profitability.
Businesses that track their spending can:
- Evaluate return on investment (ROI): Companies can determine whether their investments in marketing, new hires, or technology are yielding positive results.
- Compare cost-effectiveness: Tracking types of expenses allows businesses to compare the costs of different vendors, tools, or services, ensuring that they get the best value for their money.
- Prioritise spending: Companies can make informed decisions about where to allocate resources, focusing on the areas that drive the most growth.
6. Compliance and Financial Transparency
Tracking company expenses list ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Compliance with financial regulations ensures that companies avoid legal issues, fines, or penalties.
Proper documentation of expenditures:
- Helps in audits: Accurate records of business expenses make it easier to navigate through audits or financial reviews.
- Enhances transparency: Maintaining clear records promotes financial transparency, which is important for investors, stakeholders, or regulatory bodies.
- Ensures ethical business practices: Tracking expenses helps companies maintain integrity by ensuring that funds are used appropriately and for legitimate business purposes.
Best Practices to Manage Business Expenses
Managing business expenses efficiently is key to improving cash flow, reducing unnecessary spending, and increasing overall profitability. Here are some best practices for managing your types of expenses:
- Create and Stick to a Budget : Establishing a budget is essential for managing your company expenses. A well-crafted budget serves as a guide for how much you can spend in each category, helping you control costs and avoid overspending. Ensure to create a company expenses list to track budget effectively.
- Regularly Review Expenses : Reviewing your expenses on a regular basis allows you to stay on top of your spending and identify areas where you might cut costs. Conduct a thorough review of your budget and expenses every quarter to ensure you’re meeting financial goals.
- Automate Expense Tracking : Automating your expense tracking through accounting or expense management software can save time and increase accuracy. Automation reduces human errors and ensures that you don’t miss any important payments or deductions.
- Negotiate with Vendors : Don’t hesitate to negotiate with vendors for better pricing. Long-term relationships can often lead to discounts or more favorable payment terms, which can help reduce your overall expenses.
- Monitor Cash Flow Regularly : It’s crucial to keep a close eye on your cash flow. Monitor both incoming and outgoing funds to ensure you have enough cash on hand to cover your business expenses.
Leverage itilite for Seamless Business Travel Expense Management
Every company has expenses based on various factors and requirements in order to grow their business. These business expenses can go out of hand if not monitored properly. In order to manage a company’s travel expenses, tools such as itilite come into picture.
itilite is an advanced travel and expense management platform with state of the art features. It will help you save costs and navigate through expense management like a breeze. Moreover, the itilite expense management software has a user-friendly interface that lets users upload expense receipts and file for submissions while on the go. The smart feature automatically flags off non-compliant expenses and alerts the managers.
Schedule a free demo of itilite to learn more about our software.
















